Update Voxels
Modify voxels by raycasting to find which block the player is looking at.
Voxelize uses a fast ray-voxel intersection algorithm based on this paper.
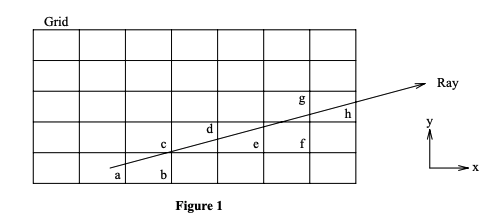
Setup Voxel Interaction
main.js
const voxelInteract = new VOXELIZE.VoxelInteract(camera, world, {
highlightType: "outline",
});
world.add(voxelInteract);
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
if (world.isInitialized) {
world.update(
camera.getWorldPosition(new THREE.Vector3()),
camera.getWorldDirection(new THREE.Vector3())
);
rigidControls.update();
voxelInteract.update();
}
renderer.render(world, camera);
}
Add a Crosshair
Update index.html:
index.html
<div id="app">
<canvas id="canvas"></canvas>
<div id="crosshair"></div>
</div>
Update style.css:
style.css
#crosshair {
width: 12px;
height: 12px;
border: 2px solid #fff3;
border-radius: 6px;
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}

Break Blocks
main.js
inputs.click("left", () => {
if (!voxelInteract.target) return;
const [x, y, z] = voxelInteract.target;
world.updateVoxel(x, y, z, 0);
});
Block type 0 is air - setting a voxel to 0 removes it.
Place Blocks
main.js
let holdingBlockType = 1;
inputs.click("middle", () => {
if (!voxelInteract.target) return;
const [x, y, z] = voxelInteract.target;
holdingBlockType = world.getVoxelAt(x, y, z);
});
inputs.click("right", () => {
if (!voxelInteract.potential) return;
const { voxel } = voxelInteract.potential;
world.updateVoxel(...voxel, holdingBlockType);
});
voxelInteract.target- The block you're looking atvoxelInteract.potential- The adjacent block position (where a new block would be placed)

Controls:
- Left click: Break block
- Middle click: Pick block type
- Right click: Place block